Welcome to the world of sugar free joy!
Low Carb Sugar-Free Sweets & Cakes
Artinci was born out of Aarti's and Sumit's (Artinci's founders) abiding love for great-tasting dessert, while helping them stay committed to their health goals as well. As a result, Artinci makes delicious desserts with zero sugar, that are science and evidence-backed.
Aarti and Sumit come from a family of three generations of diabetics. They were themselves diagnosed pre-diabetic in 2012, and right there began a lifelong quest of a healthy, active lifestyle, including healthy swaps in food
Sugar free Sweets & Cakes



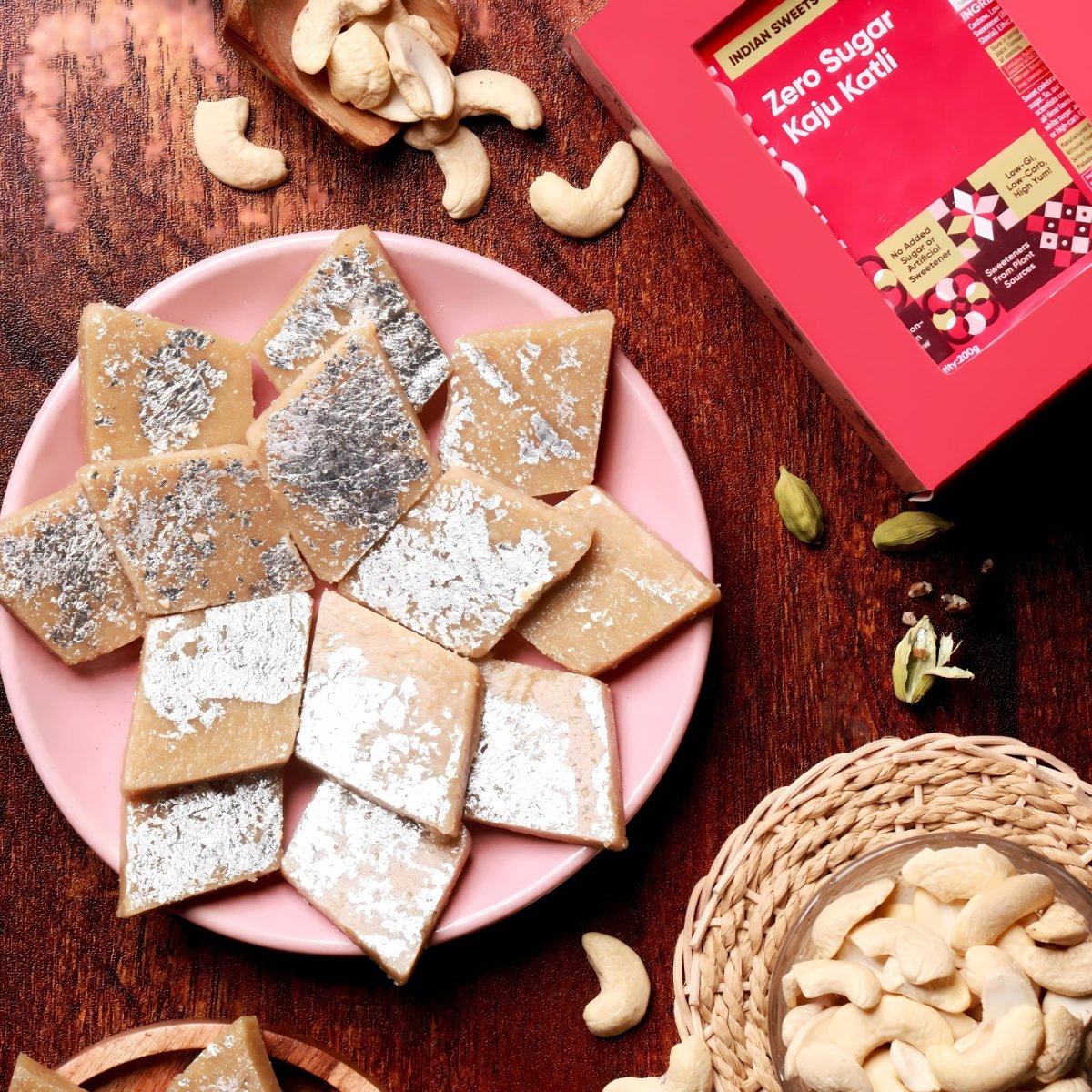
Sugar Free Kaju Katli (Stevia Sweetened) | Keto, Vegan & Diabetic Friendly Sweet | No Maltitol

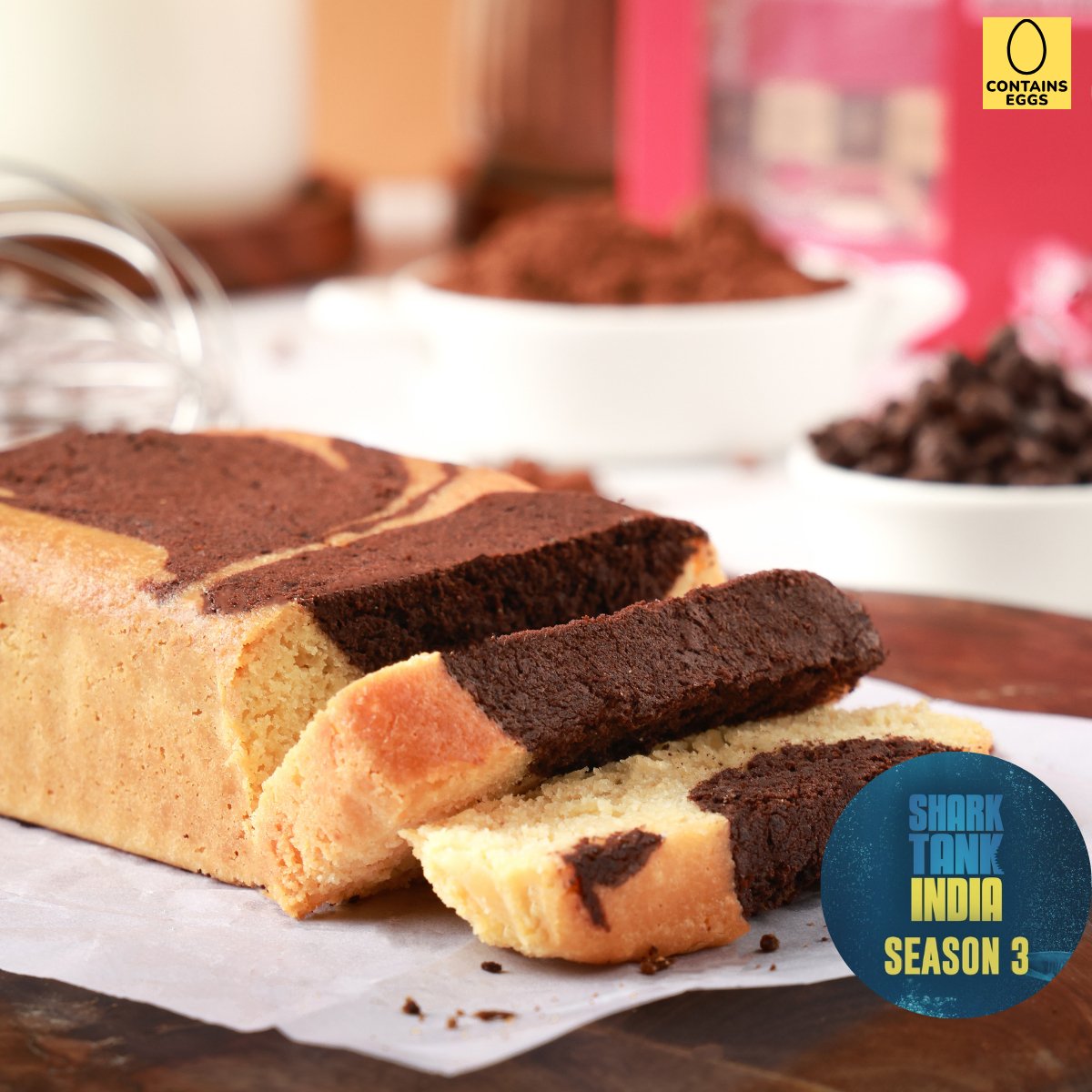
Vanilla & Chocolate Marble Sugar free Cake - Diabetic-Friendly, Keto, Gluten-Free (contains egg)



Aarti Laxman (Founder)
Artinci is founded by Aarti Laxman, a certified Metabolic coach in the Low-Carb Nutrition & Metabolic Health domain from dLife.in, India’s only legally tenable course in this subject—recognized by the NSDC (under the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship, Govt. of India). It’s also internationally accredited by the CPD Standards Office UK, with a global record of 144 CPD hours—the highest for any course of its kind. The accreditation is both nationally valid and globally recognised in over 50+ countries..
Festive Gifting in Artinci
Let customers speak for us
All about Sugar and sugar-free

Emotional eating often drives sugar cravings, turning stress or boredom into binges on sweets that spike blood sugar and worsen diabetes risk. This blog explores the gut-brain link, Indian lifestyle triggers, and practical fixes using yoga and low-GI foods for lasting control. The Gut-Brain-Sugar Connection Emotional eating hijacks the gut-brain axis, where stress hormones like cortisol signal the brain to crave sugar for quick serotonin boosts.In India, this amplifies with high-sugar chai or mithai during anxiety, leading to blood sugar crashes and fatigue.Poor gut health from processed foods worsens signals, creating a cycle tied to insulin resistance. Common Triggers in Indian Lifestyles Work deadlines prompt post-dinner gulab jamun; loneliness sparks late-night biscuit raids.Festival seasons and family gatherings normalize emotional sweets, raising obesity in 40% of urban adults.Sleep deprivation, common in Bengaluru shifts, doubles ghrelin (hunger hormone), targeting sugar. Science of Cravings Sugar floods dopamine receptors like drugs, retraining the brain for instant gratification over nutrition.Chronic emotional binges inflame the gut microbiome, slowing metabolism and hiking diabetes odds by 50%.Studies show women face 2x risk from hormonal emotional eating tied to PMS or menopause. Signs You're an Emotional Eater Cravings hit during stress, not true hunger. Eating alone or mindlessly while distracted. Guilt follows binges, fueling more cycles. Preference for sweets over savory under pressure. 5 Practical Remedies Yoga for Stress: 10-min pranayama or balasana cuts cortisol 20%, curbing 3 PM slumps. Protein First: Start meals with eggs, paneer, or dal to stabilize blood sugar and fullness. Ayurvedic Hacks: Triphala at night detoxes gut; cinnamon water tames sweet urges. Journal Triggers: Log mood before eating to spot patterns like "boredom = biscuits." Low-GI Swaps: Jowar porridge over poha; stevia lassi instead of sugary drinks. Sample Anti-Craving Meal Plan Meal Emotional Eating Swap Why It Works Breakfast Moong dal cheela + curd Fiber + protein blocks dopamine dips. Lunch Bajra roti, palak paneer Sustained energy fights afternoon crashes. Snack Nuts + jeera water Healthy fats mimic satiety of sweets. Dinner Veg khichdi + salad Light, gut-soothing to prevent night binges. Long-Term Benefits Breaking the cycle restores taste buds in 2 weeks, slashing cravings by half.Stable moods emerge from better gut health, reducing diabetes markers like HbA1c.Sustainable habits via mindfulness yield 3-5 kg loss and sharper focus for content creators. Maintenance Tips Pair with 30-min walks to burn stress sugars; limit chai to 1 tsp jaggery.Revisit journal weekly; forgive slip-ups to avoid shame spirals.For diabetics, monitor glucose post-meals to track emotional impacts.

10-Day Sugar Detox Plan for Beginners
Kickstart your journey to break free from sugar cravings with this simple, beginner-friendly 10-day detox plan. Designed for busy Indian lifestyles, it focuses on whole foods, low-GI swaps, and natural remedies to stabilize blood sugar without feeling deprived. Why Detox from Sugar? Sugar addiction mimics drug dependency by spiking dopamine and insulin, leading to crashes, fatigue, and weight gain.In India, hidden sugars in chai, namkeen, and festivals drive 77 million diabetes cases.A 10-day reset retrains taste buds, cuts inflammation, and supports gut health for long-term control. Preparation Tips Stock up on low-GI staples: millets (jowar, bajra), moong dal, paneer, eggs, ghee, stevia, nuts, and veggies like bitter gourd.Hydrate with 3-4 liters water daily; add jeera or lemon for detox.Track progress in a journal—note cravings, energy, and mood. Daily Meal Plans Day Breakfast Lunch Dinner Snacks Detox Tip 1 Moong dal cheela with green chutney Palak paneer, bajra roti, cucumber raita Vegetable khichdi with curd Handful almonds, herbal tea Drink lemon water first thing; avoid all sweets. 2 Besan omelette, tomato salad Moong dal, brown rice, bhindi sabzi Grilled chicken/fish, lauki soup Carrot sticks with hummus Chew food slowly to curb emotional eating. 3 Oats upma with veggies (no sugar) Rajma curry, quinoa, salad Tofu stir-fry, millet khichdi Yogurt with chia seeds Walk 30 mins post-meal for blood sugar control. 4 Paneer paratha (minimal atta) Chana masala, jowar roti Bottle gourd curry, dal Apple slices with peanut butter Use cinnamon tea for cravings. 5 Vegetable poha (no jaggery) Fish curry, brown rice Mixed veg sabzi, roti Boiled egg, green tea Sleep 7-8 hours; fatigue worsens cravings. 6 Sprouts salad with lemon Kadhi pakora (baked), rice Egg bhurji, palak roti Nuts mix Yoga or deep breathing for stress. 7 Dalia with nuts Paneer tikka, salad Lentil soup, bajra roti Celery with cheese Mid-detox check: energy up? Adjust portions. 8 Idli with sambar (no coconut chutney) Beetroot thoran, fish fry Cauliflower rice pulao Herbal infusion Fenugreek water overnight for insulin sensitivity. 9 Stuffed capsicum Dal makhani (low fat), quinoa Grilled veggies, paneer Berries (if available) Mindfulness: eat without screens. 10 Smoothie: spinach, curd, stevia Sabzi thali with millets Light soup, salad Dark chocolate (85%+, 1 square) Celebrate: reintroduce fruits mindfully. Craving Busters Natural Sweeteners: Stevia or monk fruit in moderation. Ayurvedic Aids: Bitter gourd juice, triphala for detox; turmeric milk at night. Habits: Protein + fiber every meal (e.g., eggs + veggies); distract with hobbies during peak cravings (3-5 PM). Expected Benefits By day 3, cravings drop 50% as taste buds adapt.Week 2 brings stable energy, better sleep, and 2-5 kg loss from reduced inflammation.Long-term: lower diabetes risk, improved gut microbiome via fiber-rich Indian foods. Post-Detox Maintenance Reintroduce natural sugars (fruits, jaggery sparingly) after day 10.Aim for <25g added sugar daily; read labels on packaged foods.Repeat quarterly or pair with intermittent fasting for sustained results.

Best Exercises After Meals Besides Walking
Light exercises after meals, like yoga or cycling, effectively blunt blood sugar spikes by boosting muscle glucose uptake, ideal for diabetes management beyond basic walking. Yoga poses and bodyweight moves timed 30 minutes post-meal align with glucose peaks, enhancing insulin sensitivity more effectively than pre-meal activity. These low-impact options fit home or office settings, reducing HbA1c over time when consistent. Top Alternatives Exercise Duration & Timing Key Benefit Indian Fit Chair Yoga (twists, leg lifts) 10-15 min, 30 min after Improves digestion, 20% spike drop Seniors, office desks Bodyweight Squats/Lunges 10 min (2x10 reps), 30 min after Muscle glucose sink, sustained control Home, no equipment Stationary Cycling 15-20 min moderate, 30-45 min after Cardio burn without joint stress Apartments, gyms Seated Arm Circles/Torso Twists 5-10 min continuous, right after Boosts circulation, low effort Post-lunch deskside Light Swimming Strokes (pool or mimic) 15 min, 30 min after Full-body, neuropathy-safe Community pools Start with 10 minutes to avoid GI discomfort, monitor glucose pre/post, and combine with low-GI foods like millets for amplified effects. Ideal for your bilingual blogs targeting metabolic health. https://www.eatingwell.com/best-time-exercise-for-optimal-glucose-control-after-meals-11903191 https://www.perplexity.ai/search/6e7abbb1-f4b6-44be-8fdb-b60ec0a00b89 https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11053955/

Long-term A1C Benefits from Consistent Post-Meal Activity Routines
Consistent post-meal activity routines, like 15-minute walks after each meal, significantly lower HbA1c levels in type 2 diabetes patients by improving glycemic control over time. These routines outperform one-time daily exercise, reducing average blood glucose and long-term complications without increasing hypoglycemia risk. Post-meal exercise enhances insulin sensitivity and muscle glucose uptake, leading to sustained HbA1c drops as shown in trials where 15 minutes after each meal improved profiles more than 45-minute daily sessions. Over months, this blunts chronic postprandial hyperglycemia, a key HbA1c driver, cutting cardiovascular risks. Indian-Friendly Routine Example Meal Activity (15-30 min) Timing Expected Benefit Breakfast (roti-sabzi) Brisk walk or yoga twists 30 min after Peak glucose tame Lunch (dal-chawal) Cycling or squats 30 min after Midday spike cut Dinner Light kabaddi or stretches 30-45 min after Overnight stability Total: 45-90 min/day, yielding 0.5-1% HbA1c reduction in studies. Track via glucometer, pair with low-GI millets, and consult doctors for insulin users to personalize. https://diabetes.org/health-wellness/fitness/blood-glucose-and-exercise https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11053955/ https://www.eatingwell.com/best-time-exercise-for-optimal-glucose-control-after-meals-11903191