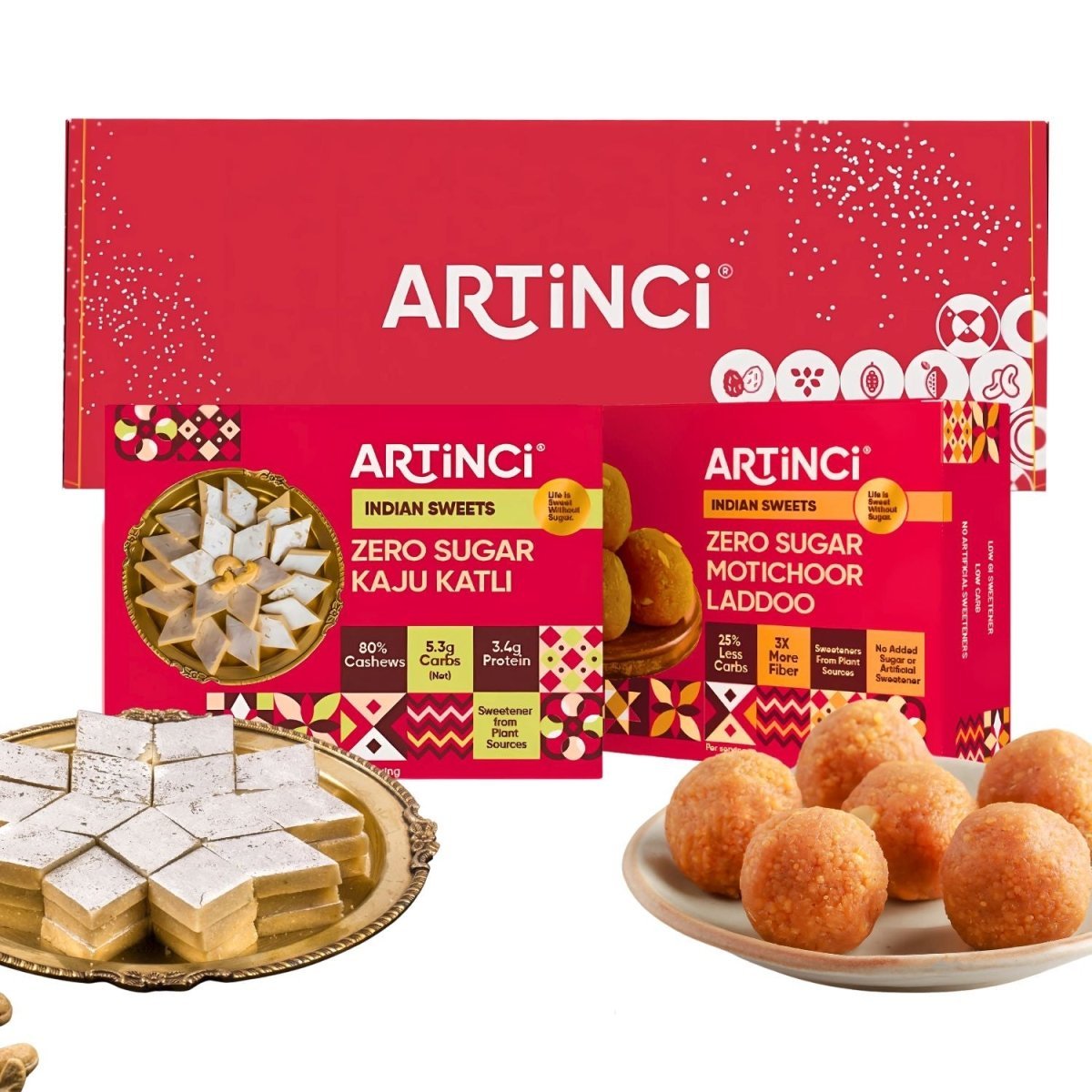
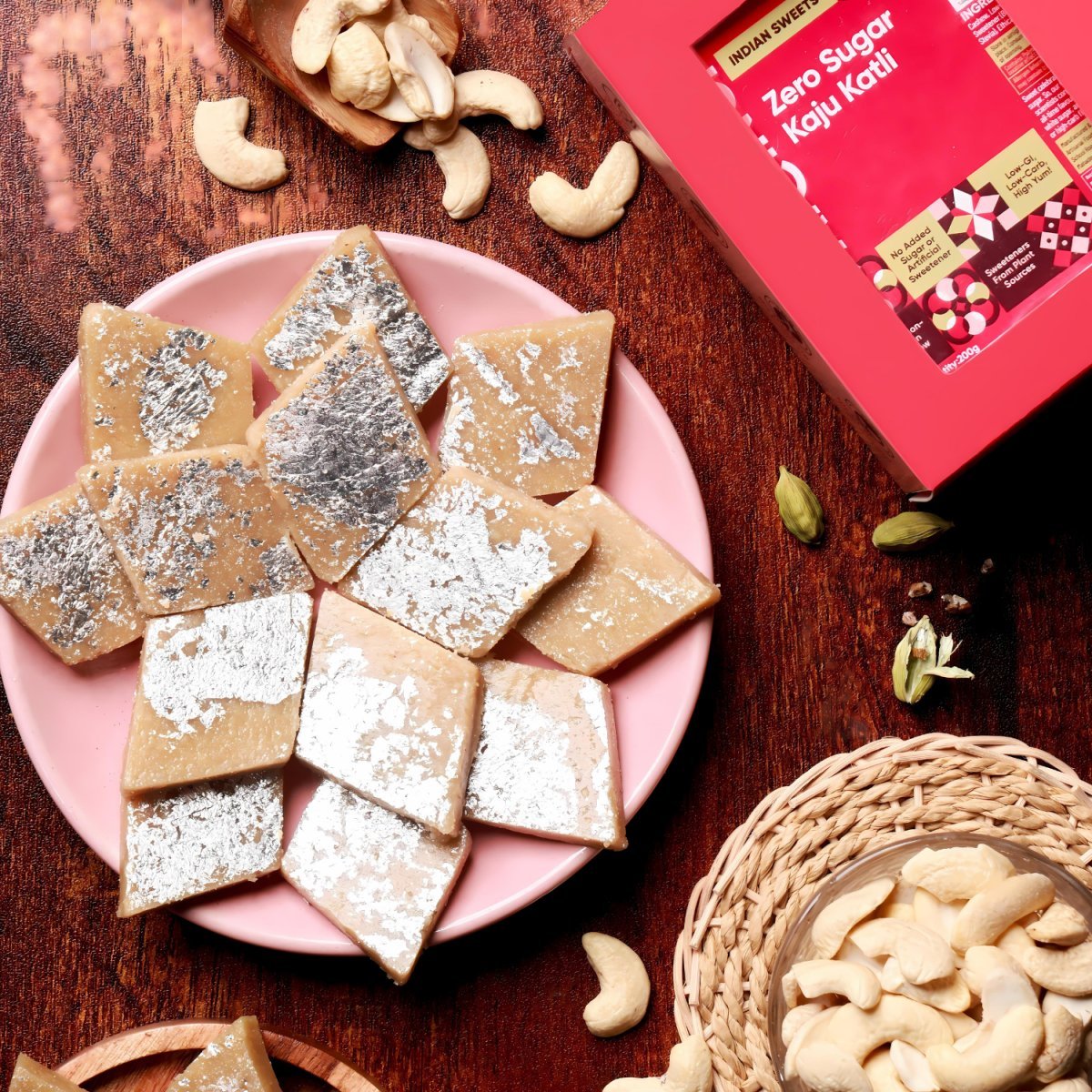
Welcome to the world of sugar free joy!
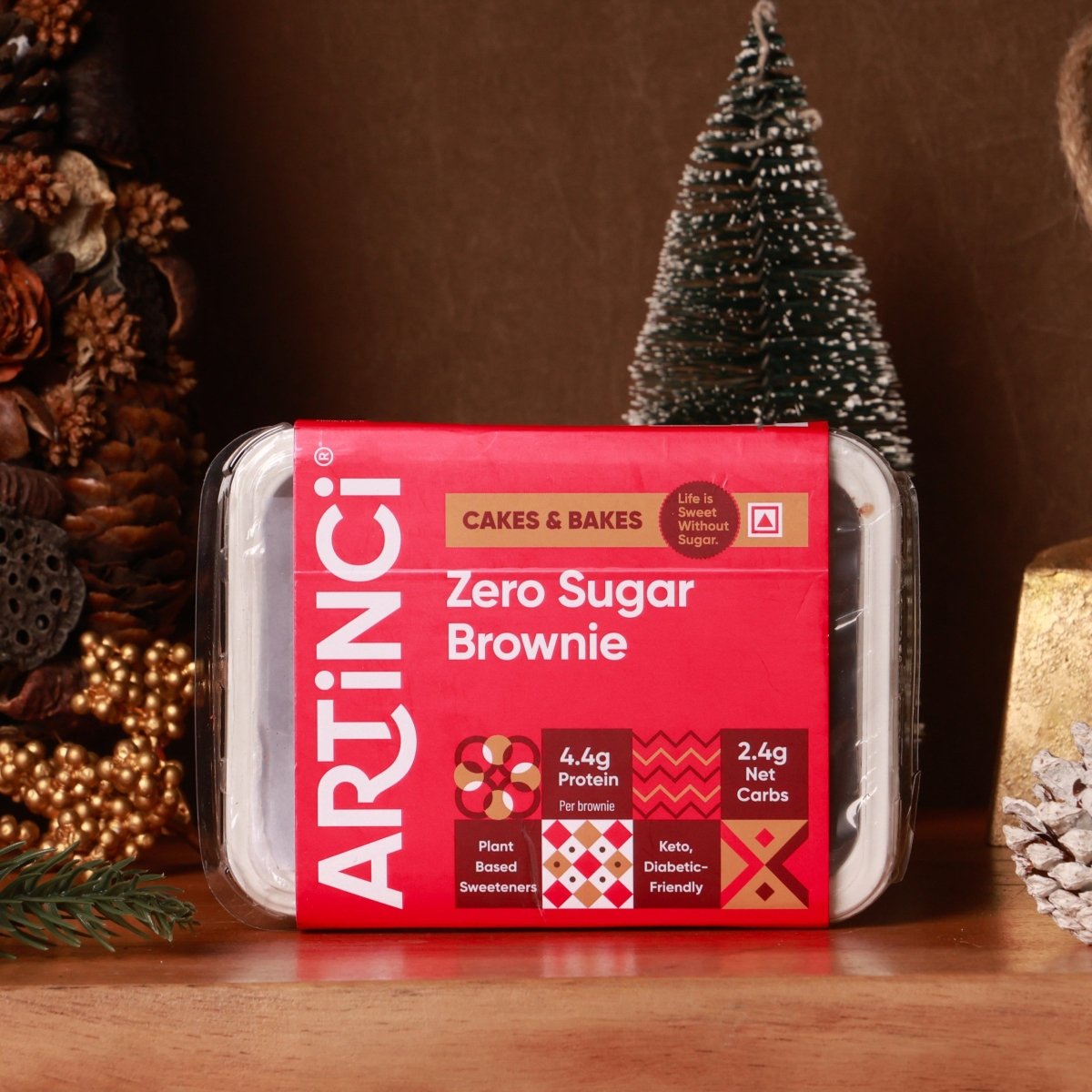
Low Carb Sugar-Free Desserts & Snacks
Artinci was born out of Aarti's and Sumit's (Artinci's founders) abiding love for great-tasting dessert, while helping them stay committed to their health goals as well. As a result, Artinci makes delicious desserts with zero sugar, that are science and evidence-backed.
Aarti and Sumit come from a family of three generations of diabetics. They were themselves diagnosed pre-diabetic in 2012, and right there began a lifelong quest of a healthy, active lifestyle, including healthy swaps in food
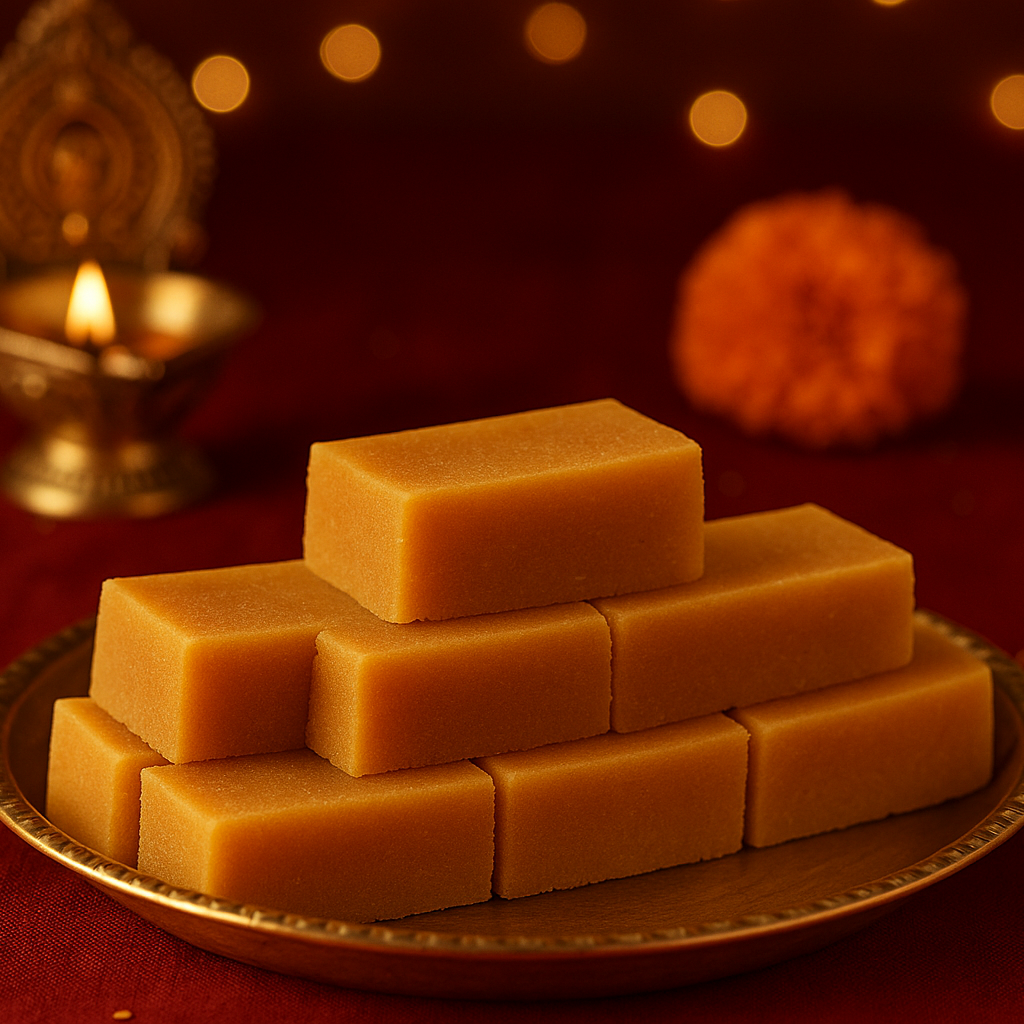
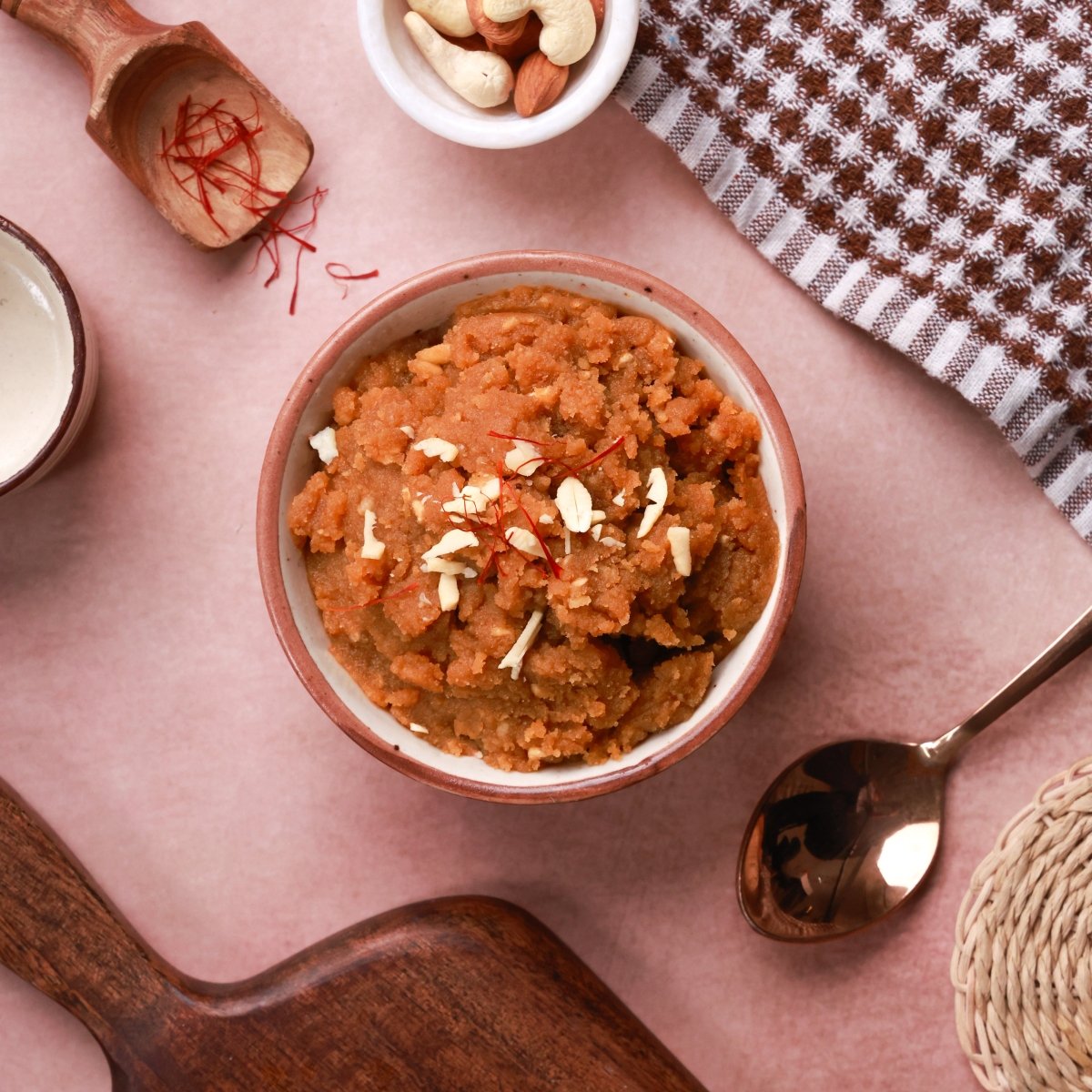
Indulgent Halwas & Cozy Cakes
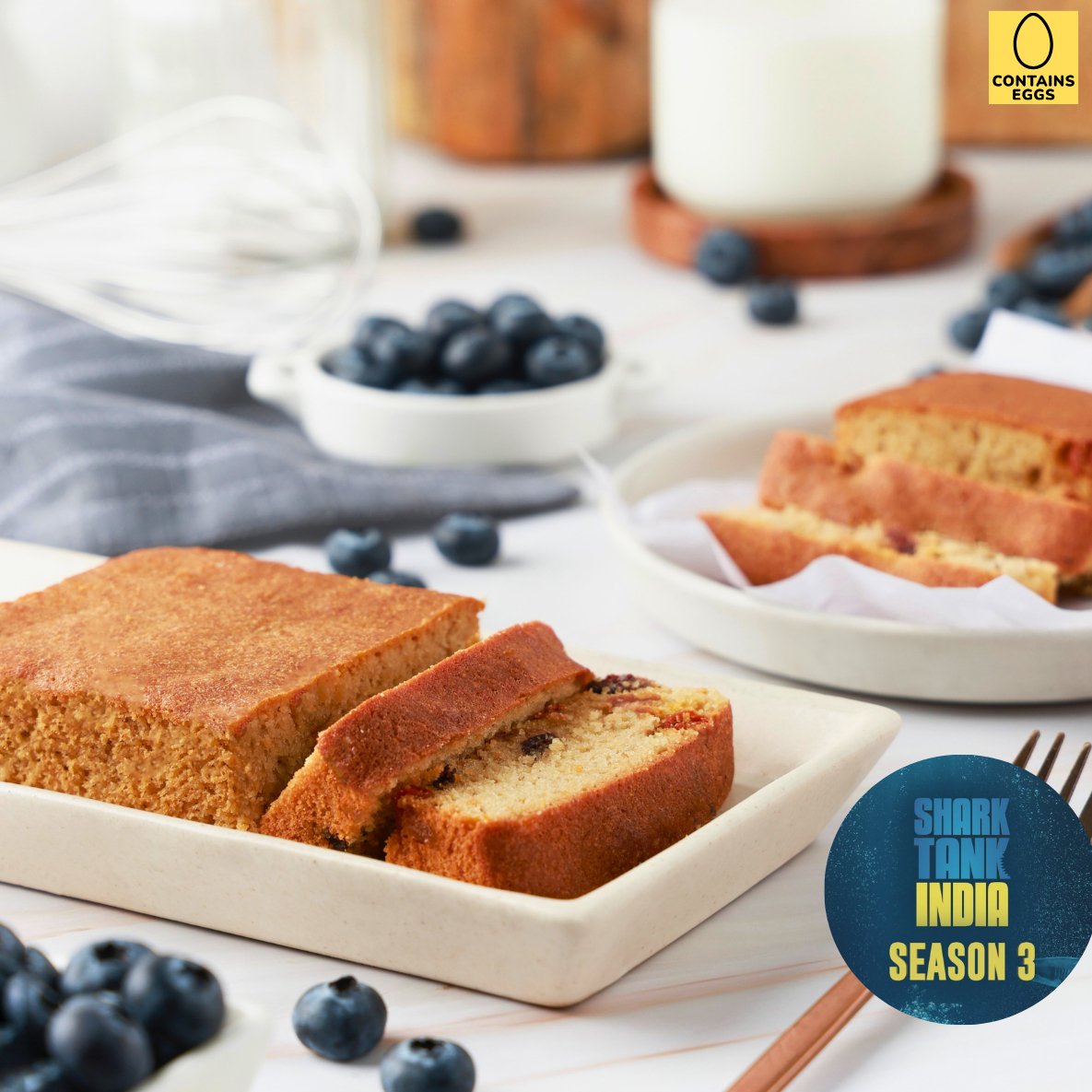





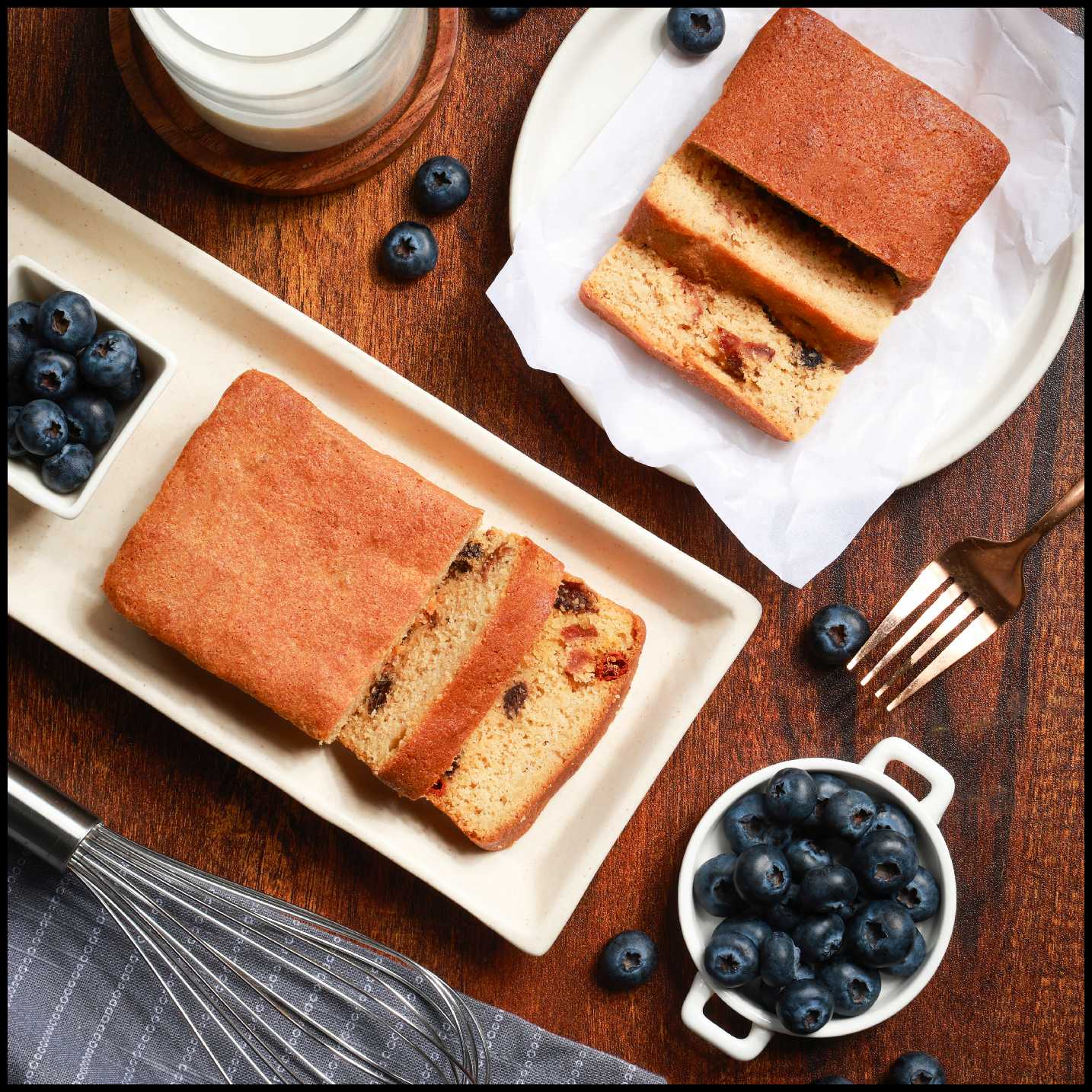
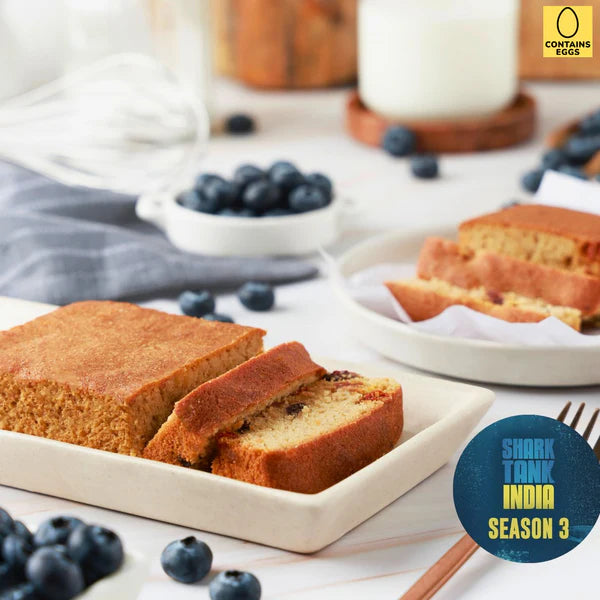
Berries Almond Cake - Sugar-Free, Keto, Gluten-Free, Diabetic-friendly (contains egg)
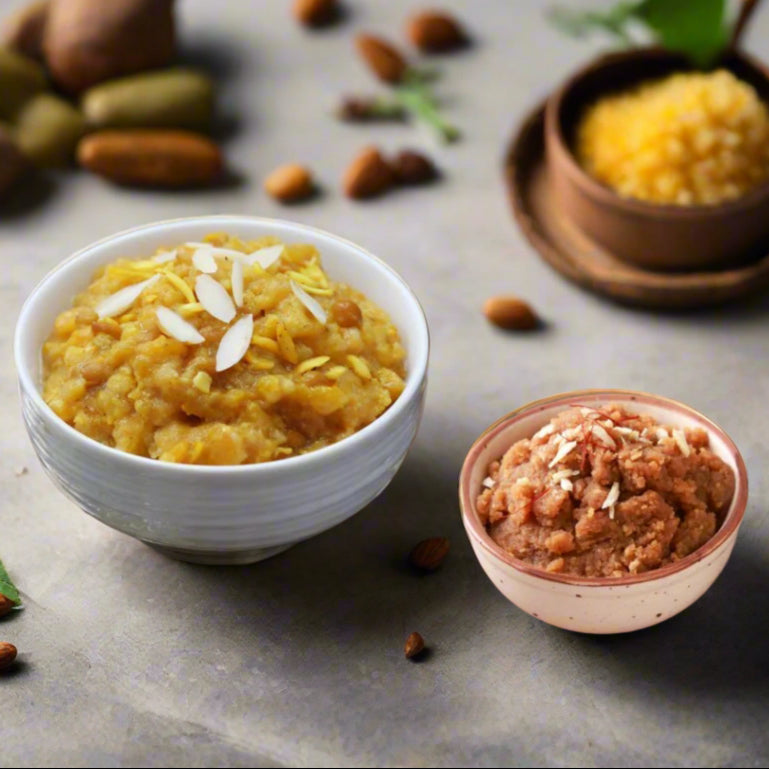



Sugar free Halwa combo @499



Aarti Laxman (Founder)
Artinci is founded by Aarti Laxman, a certified Metabolic coach in the Low-Carb Nutrition & Metabolic Health domain from dLife.in, India’s only legally tenable course in this subject—recognized by the NSDC (under the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship, Govt. of India). It’s also internationally accredited by the CPD Standards Office UK, with a global record of 144 CPD hours—the highest for any course of its kind. The accreditation is both nationally valid and globally recognised in over 50+ countries..
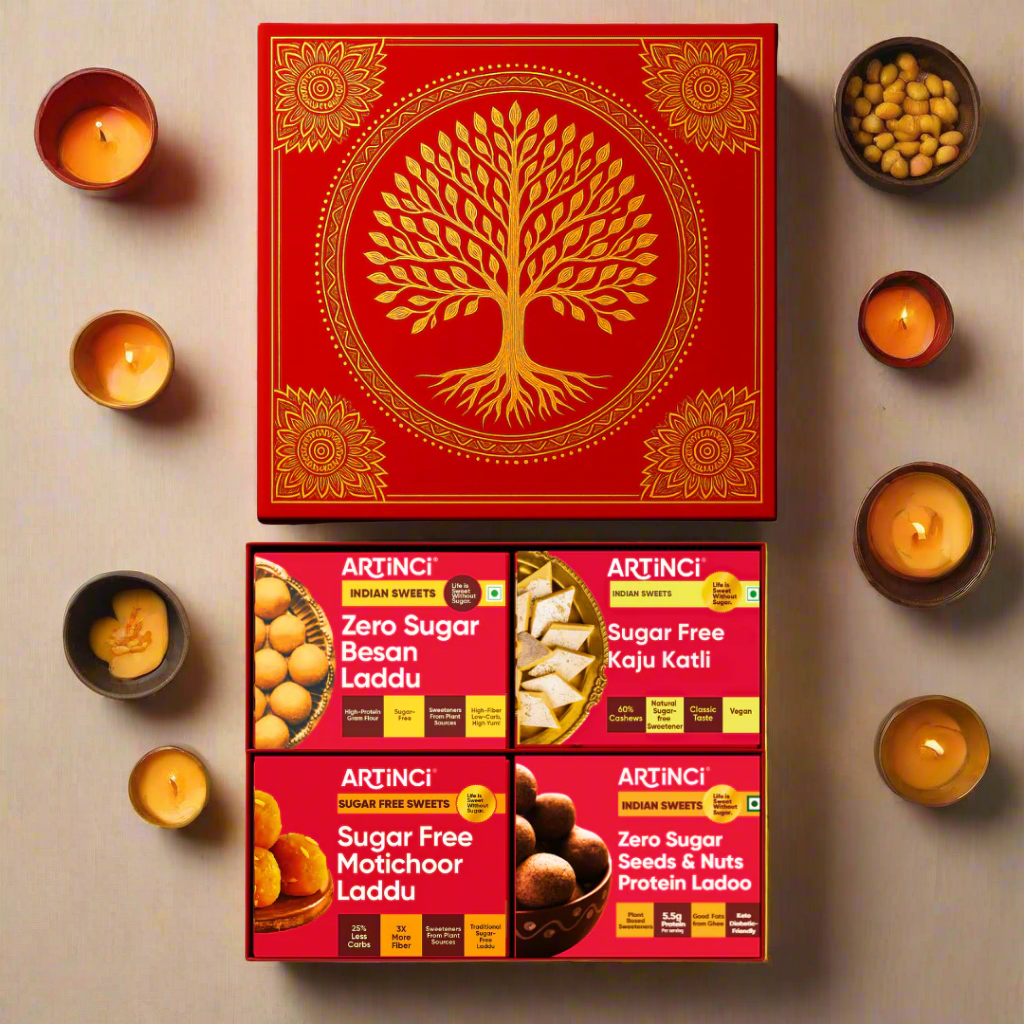
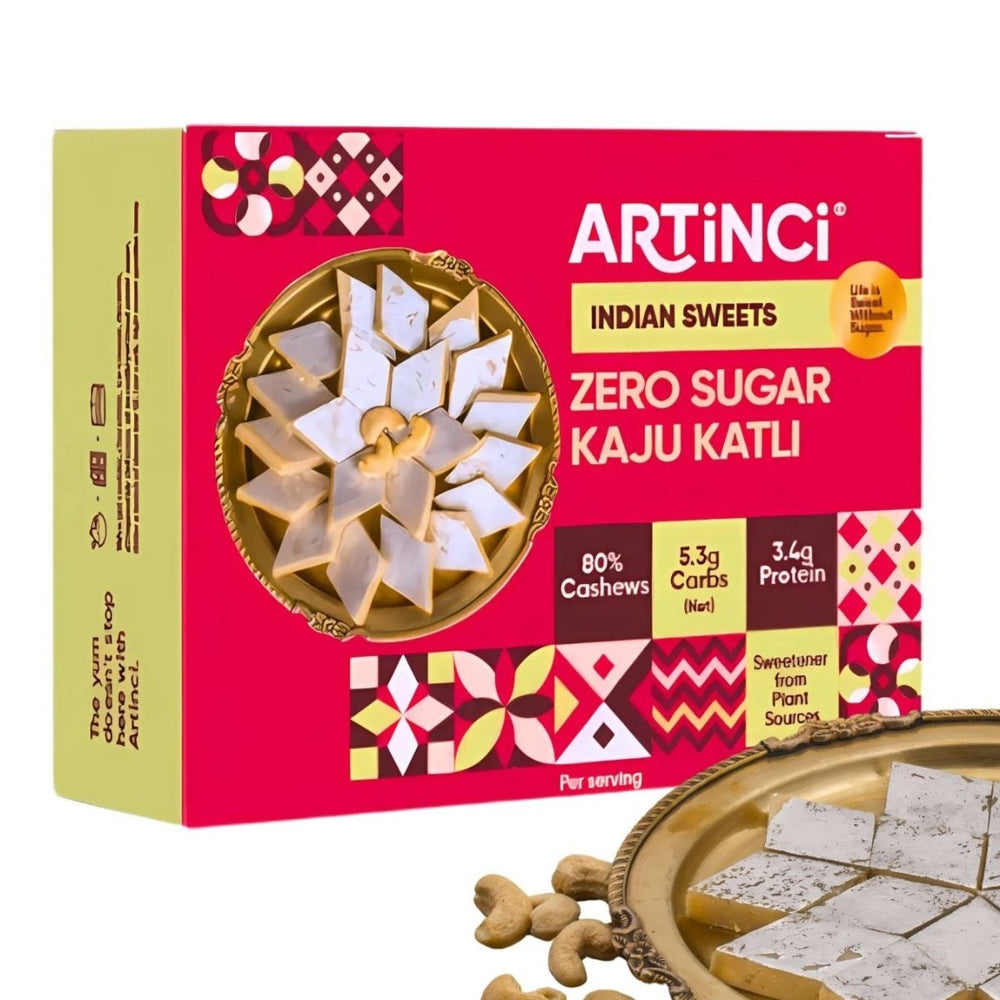
Festive Gifting in Artinci
Let customers speak for us
All about Sugar and sugar-free

Consuming sugar-free sweets daily is generally considered safe when done in moderation, especially for individuals managing diabetes or aiming to reduce sugar intake, but overconsumption can cause digestive discomfort for some people and may impact overall health. It's best to treat sugar-free sweets as occasional treats rather than daily staples to avoid potential gut issues and support long-term healthy habits. Should Sugar-Free Sweets Be Eaten Daily? Sugar-free sweets provide sweetness without the blood sugar spikes of traditional sugar and may fit better in a diabetic or calorie-controlled diet. However, many sugar-free treats rely on sugar alcohols like erythritol, sorbitol, or artificial sweeteners. Consuming high amounts can cause digestive discomfort (gas, bloating, diarrhea) for some people. Long-term, daily use of artificial sweeteners has produced mixed study results—some link it to higher risk of stroke and heart disease, though evidence is not fully conclusive and may depend on other lifestyle factors. Additionally, most sugar-free treats are still processed foods with little nutritional value, so they're best enjoyed as an occasional treat, not a staple. Practical Guidelines Moderation is key: Enjoying sugar-free sweets in moderate portions a few times a week is unlikely to pose health risks for most people. Read labels for sweetener content and calories; sugar-free does not always mean calorie-free. If you notice digestive symptoms, decrease your intake or try different sweeteners. Focus on whole, nutrient-rich foods for daily snacks, reserving sugar-free sweets for special occasions or mindful treats. Cultural Context: Festivals and Diabetes During festivals and special occasions, sugar-free sweets can be a valuable alternative for those managing diabetes, allowing participation without excessive sugar intake. Making them a daily habit, however, remains debatable—research suggests that the healthiest approach is diversity in snack choices and moderation for all treats, sugar-free or otherwise. In conclusion, sugar-free sweets are best reserved for occasional enjoyment. While suitable for those with diabetes or those avoiding sugar, moderation helps avoid digestive discomfort and supports overall health. References: https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/artificial-sweeteners/art-20046936 https://www.prevention.com/food-nutrition/a65503074/the-truth-about-sugar-free-candy/ https://www.verywellhealth.com/pros-and-cons-of-sugar-free-candy-1087139 https://www.parkview.com/blog/the-sour-side-of-sugar-free-candy
Do Artificial or Natural Sweeteners Like Sucralose, Stevia, or Monk Fruit Have Any Side Effects?
Artificial and natural sweeteners like sucralose, stevia, and monk fruit are commonly used as sugar substitutes and are generally recognized as safe for most people when consumed within recommended guidelines. However, each type of sweetener may have specific side effects or considerations. Understanding Sweetener Side Effects Artificial and natural sweeteners are favored for their low- or zero-calorie properties, but their safety profiles and potential side effects differ. Sucralose Sucralose (often known by the brand name Splenda) is widely used in processed foods and beverages. While it is considered safe by regulatory authorities, studies on animals suggest potential links to blood sugar fluctuations and even cancer when consumed in large quantities over a lifetime. Some human studies also report possible alterations in gut microbiota, which can affect glucose tolerance. More research is needed to determine long-term safety in humans. Stevia Stevia is a plant-based sweetener known for being much sweeter than sugar with zero calories and carbohydrates. Most regulatory bodies consider high-purity stevia extracts safe, but some people report gastrointestinal symptoms like gas, bloating, or nausea after consumption. Allergic reactions are rare but possible in sensitive individuals. Stevia is also sometimes mixed with sugar alcohols, which may increase the risk of digestive side effects. Monk Fruit Monk fruit sweetener is another natural, zero-calorie option made from the fruit native to southern China. Research indicates that monk fruit extract is generally safe, with minimal or no reported side effects in animal and human studies so far. However, it is less widely studied, especially regarding long-term use and effects in special populations like pregnant women. Like stevia, monk fruit is sometimes blended with other ingredients that can affect its safety profile. Key Points for Health-Conscious Consumers Sucralose may alter gut bacteria and has shown negative effects in animal studies—consume in moderation and keep up with ongoing research. Stevia is plant-based, but can cause gastrointestinal symptoms for some people, especially if mixed with sugar alcohols. Monk fruit appears safest but is more expensive and less studied long-term; check product labels for added ingredients and consider personal tolerance. Always follow acceptable daily intake recommendations and consult a healthcare professional, especially if you have underlying health concerns or are pregnant. By choosing wisely and observing how your body responds, you can enjoy the benefits of sugar substitutes while minimizing potential side effects. Reference: https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/artificial-sweeteners/art-20046936 https://www.cspi.org/article/which-low-calorie-sweeteners-are-safe-and-which-arent https://www.medicinenet.com/is_monk_fruit_safe_and_healthier_than_stevia/article.htm https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/322769 https://www.foodandnutritionjournal.org/volume13number1/the-battle-of-natural-sweeteners-a-comprehensive-guide-to-monk-fruit-and-stevia/

Can Eating Sugar-Free Sweets Help in Weight Management, or Does Excess Lead to Health Risks?
Sweet cravings are universal, but for diabetics and health-conscious folks, giving in often brings more worry than pleasure. Enter sugar-free sweets—promoted as low-calorie, diet-friendly, and “guiltless” treats. But do they really deliver weight loss, or can too much be a setback? The Science: How Sugar-Free Sweets Support Weight Management Sugar-free alternatives, especially those using approved low or no-calorie sweeteners, can reduce overall calorie intake compared to sugar-heavy desserts. Multiple controlled studies find that substituting sugar with sweeteners leads to modest weight loss for most people, particularly when used as part of a balanced diet. Sugar-free options allow you to satisfy cravings with fewer calories, which may help control portions and maintain a healthy weight. Sugar-free snacks also tend to have a lower glycaemic impact, so they can help stabilize blood sugar—a significant benefit for people with diabetes or those aiming to prevent sugar spikes. What Can Go Wrong With Overconsumption? However, sugar-free does not mean “eat as much as you want.” Overindulging brings hidden dangers: Eating excessive sugar-free sweets still adds to daily calories, possibly leading to weight gain if you’re not mindful of portions. Many sugar-free treats contain sugar alcohols (like maltitol, erythritol), which in large amounts cause bloating, gas, or diarrhea. Relying on these sweets may lead to eating less nutrient-rich foods, undermining overall diet quality. There’s also a psychological pitfall: the “health halo” effect. Belief that sugar-free equals healthy may lead people to eat larger portions or snack more often, undercutting any calorie savings. Practical Tips for Safe Enjoyment Treat sugar-free sweets as occasional indulgences, not daily staples. Always check for fat, calorie, and ingredient lists—“sugar-free” doesn’t guarantee low calorie or high nutrition. Choose products using natural sweeteners, such as stevia or monk fruit, and avoid artificial colors or unhealthy fats. For diabetics, track both carbohydrate and calorie counts to keep blood sugar steady. The Takeaway Sugar-free sweets can fit into weight management plans and provide peace of mind for diabetics—when enjoyed in moderation. Mindful eating, portion control, and reading nutrition labels are key to reaping benefits while avoiding unexpected health risks. Reference: https://www.sweeteners.org/benefits-in-weight-management/ https://medicinehealth.leeds.ac.uk/faculty-/news/article/680/sweeteners-can-improve-weight-loss-maintenance-new-research-suggests https://www.artinci.com/blogs/news/can-sugar-free-desserts-aid-in-portion-control-for-weight-loss https://netrition.com/blogs/netrition-blog/will-sugar-free-candy-stall-my-weight-loss https://www.healthline.com/health/food-nutrition/sugar-facts-scientific https://www.artinci.com/blogs/news/can-sugar-free-desserts-aid-in-portion-control-for-weight-loss

Exercise and Diet: The Perfect Pair for Optimal Health
Exercise and diet truly go hand in hand in shaping health and well-being. Balancing both is key to achieving sustainable fitness, effective weight management, and optimal quality of life. How Diet Fuels Exercise Consuming a nutritious diet provides the energy needed for daily activities and workouts. Whole foods rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats enhance endurance and recovery while supporting immune function. Mindful portion control and a focus on nutrient-dense foods lay the foundation for better health, fueling your muscles and brain for everyday challenges. Exercise Powers Results Engaging in regular physical activity elevates calorie expenditure, boosts metabolism, and helps maintain lean muscle mass. Activities like jogging, cycling, and strength training not only burn calories but also improve cardiovascular health and mental well-being. Exercise helps regulate hunger, aids in fat loss while preserving muscle, and increases the body’s ability to manage glucose and lipids. The Synergy: Why Both Matter Studies consistently show that combining exercise routines with a balanced diet brings greater health benefits than relying on either one alone. The best results for weight management, metabolic health, and long-lasting well-being come from this partnership. Efforts to lose weight or improve fitness are most effective and sustainable when both pillars are addressed together. Practical Tips for Balance Choose whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables for lasting energy. Schedule regular physical activities you enjoy, aiming for at least 150 minutes per week. Practice mindful eating—watch portions and avoid processed foods. Stay hydrated and time your meals to support your workouts. Together, exercise and diet form a powerful duo for vibrant health, disease prevention, and lifelong vitality. References: https://www.linkedin.com/posts/expatinsure_understand-the-link-between-diet-and-exercise-activity-7271124754944724993-ZU0K https://sprintmedical.in/blog/exercising-and-right-diet-go-hand-in-hand-in-weight-loss https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/diet-vs-exercise https://sprintmedical.in/blog/exercising-and-right-diet-go-hand-in-hand-in-weight-loss https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC416564/