Welcome to the world of sugar free joy!
Low Carb Sugar-Free Sweets & Cakes
Artinci was born out of Aarti's and Sumit's (Artinci's founders) abiding love for great-tasting dessert, while helping them stay committed to their health goals as well. As a result, Artinci makes delicious desserts with zero sugar, that are science and evidence-backed.
Aarti and Sumit come from a family of three generations of diabetics. They were themselves diagnosed pre-diabetic in 2012, and right there began a lifelong quest of a healthy, active lifestyle, including healthy swaps in food
Sugar free Sweets & Cakes



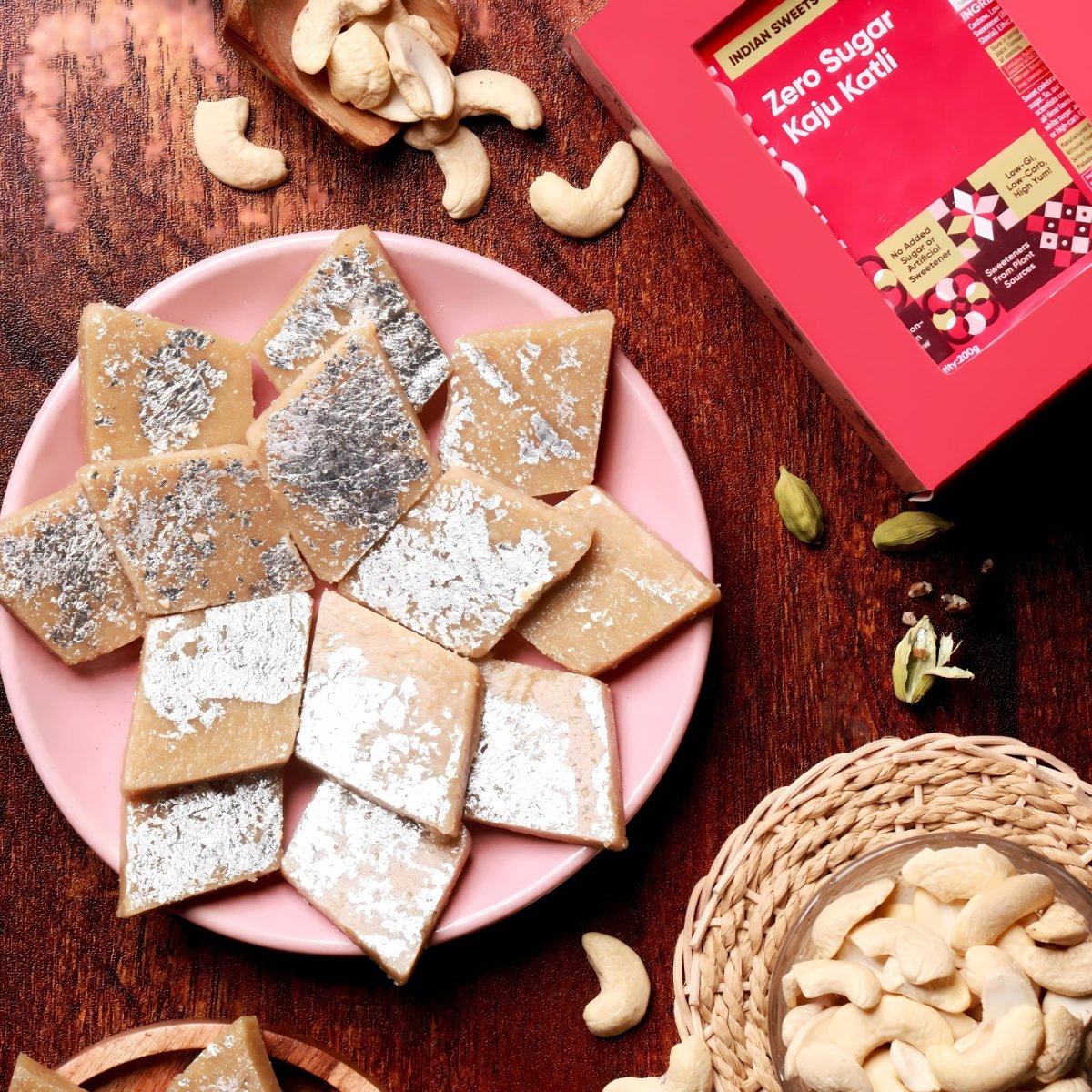
Sugar Free Kaju Katli (Stevia Sweetened) | Keto, Vegan & Diabetic Friendly Sweet | No Maltitol

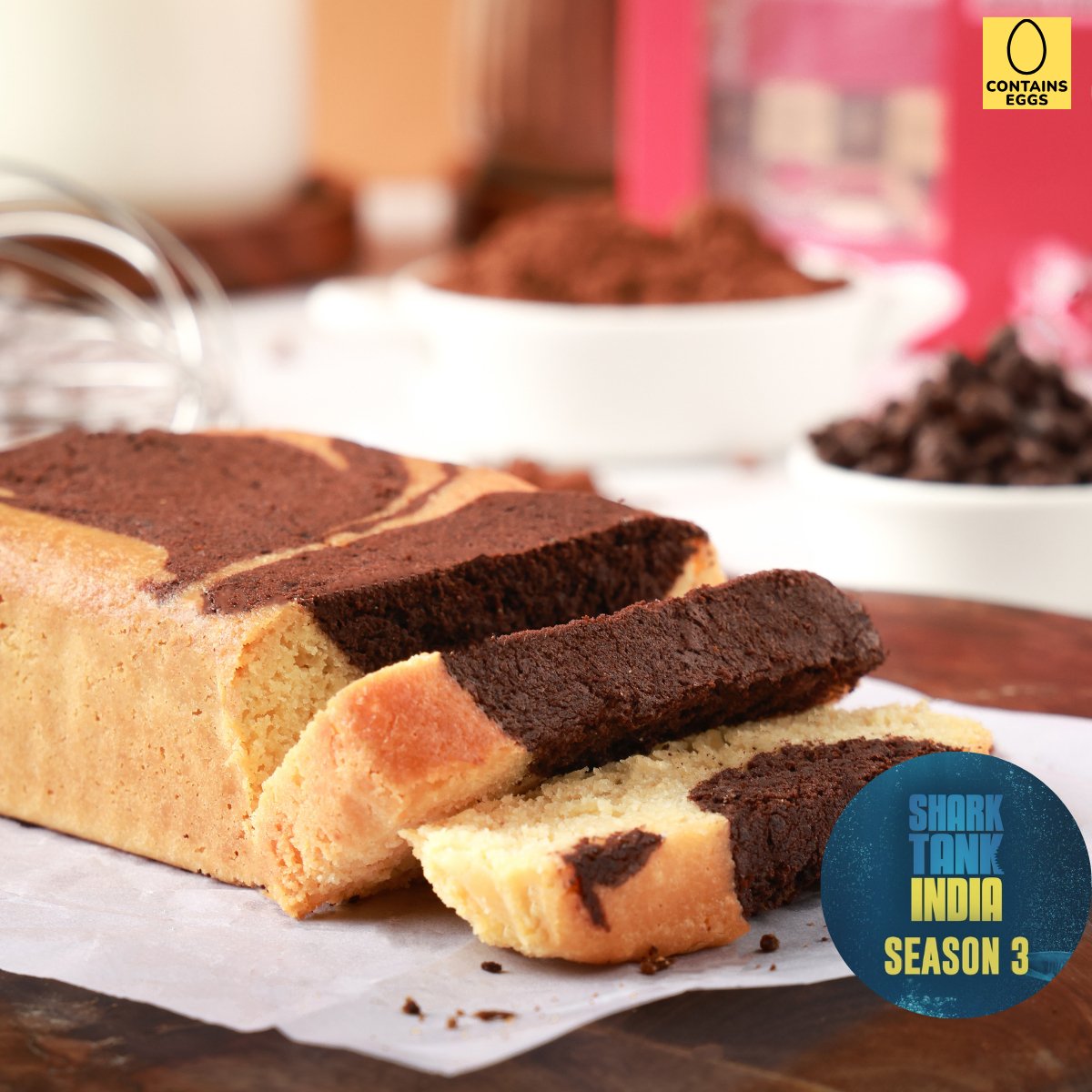
Vanilla & Chocolate Marble Sugar free Cake - Diabetic-Friendly, Keto, Gluten-Free (contains egg)



Aarti Laxman (Founder)
Artinci is founded by Aarti Laxman, a certified Metabolic coach in the Low-Carb Nutrition & Metabolic Health domain from dLife.in, India’s only legally tenable course in this subject—recognized by the NSDC (under the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship, Govt. of India). It’s also internationally accredited by the CPD Standards Office UK, with a global record of 144 CPD hours—the highest for any course of its kind. The accreditation is both nationally valid and globally recognised in over 50+ countries..
Festive Gifting in Artinci
Let customers speak for us
All about Sugar and sugar-free

परिचय प्रोटीन आमतौर पर ब्लड शुगर को स्थिर रखने में मदद करता है, क्योंकि यह कार्ब्स के पाचन को धीमा करता है। लेकिन व्हे और हाइड्रोलाइज्ड प्रोटीन पाउडर डायबिटीज मरीजों में अप्रत्याशित स्पाइक पैदा कर सकते हैं। यह ब्लॉग बताएगा क्यों ऐसा होता है और सुरक्षित विकल्प क्या हैं। प्रोटीन के सामान्य लाभ प्रोटीन भोजन के बाद ग्लूकोज रिलीज को धीमा करके ब्लड शुगर स्पाइक रोकता है। अध्ययनों में पाया गया कि हर मील में 20-30g प्रोटीन पोस्टप्रैंडियल शुगर को 40% तक कम कर सकता है। डायबिटीज में यह मसल्स बनाए रखने और भूख कंट्रोल करने में उपयोगी है। व्हे प्रोटीन स्पाइक क्यों करता है? व्हे तेजी से पचने वाला दूध प्रोटीन है, जो BCAA अमीनो एसिड्स (लीसिन, आइसोलीसिन) से भरपूर होता है। ये इंसुलिन स्राव को तेज करते हैं—कभी-कभी सफेद ब्रेड से भी ज्यादा। अध्ययन दिखाते हैं कि व्हे GIP और GLP-1 हार्मोन बढ़ाता है, जो इंसुलिन स्पाइक लाता है। डायबिटीज में खराब इंसुलिन सेंसिटिविटी के कारण यह ग्लूकोज में बदल सकता है। हाइड्रोलाइज्ड प्रोटीन का खतरा हाइड्रोलाइज्ड प्रोटीन पहले से टूटा हुआ होता है, जो अल्ट्रा-फास्ट अब्जॉर्प्शन देता है। इससे 50-60% प्रोटीन ग्लूकोज में बदल जाता है, ब्लड शुगर को 92 से 255 तक उड़ा सकता है। CGM डेटा में यह पोस्टप्रैंडियल स्पाइक दिखाता है। डायबिटीज मरीजों के लिए बेहतर विकल्प धीमे पचने वाले प्रोटीन चुनें जो कम इंसुलिन स्पाइक दें: केसीन ब्लेंड: व्हे से धीमा, लंबे समय तक स्थिर रखता है। प्लांट-बेस्ड: टोफू (10g प्रोटीन/100g, कम GI), चने, राजमा, मूंग दाल—ब्लड शुगर स्थिर रखते हैं। भारतीय स्रोत: पनीर (18g/100g), अंडे, सोया चंक्स, स्प्राउट्स—कम कार्ब्स, हाई फाइबर।ये लो-GI हैं और किडनी हेल्थ सपोर्ट करते हैं। प्रोटीन प्रकार स्पाइक रिस्क ब्लड शुगर प्रभाव भारतीय उदाहरण प्रोटीन प्रकार स्पाइक रिस्क ब्लड शुगर प्रभाव भारतीय उदाहरण व्हे उच्च तेज इंसुलिन स्पाइक - हाइड्रोलाइज्ड बहुत उच्च 50-60% ग्लूकोज रूपांतरण - केसीन निम्न स्थिर रिलीज दही प्लांट प्रोटीन निम्न कम GI टोफू, दालें पनीर/अंडे निम्न धीमा पाचन पनीर भुर्जी भारतीय डाइट में टिप्स नाश्ते में पनीर पराठा या दाल चीला लें—25g प्रोटीन मिलेगा बिना स्पाइक। जिम के बाद स्प्राउट्स सलाद या सोया करी चुनें। CGM से मॉनिटर करें। सप्लीमेंट्स: Nestle Resource Diabetic या Vidavance जैसे लो-GI पाउडर। डॉक्टर से सलाह लें। निष्कर्ष व्हे और हाइड्रोलाइज्ड प्रोटीन तेज पाचन से स्पाइक करते हैं, लेकिन प्राकृतिक भारतीय प्रोटीन जैसे दालें, पनीर सुरक्षित हैं। डायबिटीज मैनेजमेंट में CGM यूज करें और डॉक्टर से कंसल्ट करें। स्वस्थ रहें! https://www.yourdiabetesinsider.com/blog/protein-powder-spikes-blood-sugar https://www.naturagenesis.com/top-10-diabetic-powders-in-india/ https://pescience.com/blogs/articles/whey-protein-insulin-spikes-and-how-to-avoid-them https://www.eatingwell.com/best-heart-healthy-proteins-for-diabetes-8775714 https://karger.com/anm/article/69/1/56/42555/Insulinotropic-Effects-of-Whey-Mechanisms-of

नाइट-टाइम प्रोटीन स्नैक्स: क्या ये फास्टिंग ग्लूकोज और सुबह के ब्लड शुगर स्पाइक्स को कम कर सकते हैं?
रात में प्रोटीन युक्त स्नैक्स लेना फास्टिंग ब्लड शुगर को स्थिर रखने और सुबह के स्पाइक्स रोकने में मदद करता है। ये स्नैक्स ग्लूकोज प्रोडक्शन को नियंत्रित करते हुए रक्त शर्करा को संतुलित रखते हैं। डायबिटीज वाले भारतीयों के लिए ये आसान और प्रभावी हैं। प्रोटीन का रात में प्रभाव रात में प्रोटीन लेने से ग्लूकोनियोजेनेसिस कम होता है, जो सुबह खाली पेट ग्लूकोज बढ़ाता है। केसिन जैसे स्लो-डाइजेस्टिंग प्रोटीन रक्त शर्करा को 4-6 घंटे स्थिर रखते हैं। अध्ययनों से पता चलता है कि 20-30g प्रोटीन रात के स्नैक्स फास्टिंग लेवल को 10-20 mg/dL तक कम कर सकते हैं। 5 आसान भारतीय रेसिपीज पनीर टिक्का स्नैक (25g प्रोटीन) 100g कम फैट पनीर को दही-मसालों में मैरिनेट कर ग्रिल करें। पालक के साथ सर्व करें। रेडी इन 15 मिनट। ग्रीक दही विद बादाम (22g प्रोटीन) 200g अनस्वीटन्ड ग्रीक योगर्ट में 10 बादाम और चिया सीड्स मिलाएं। फाइबर स्पाइक्स रोकता है। उबले अंडे विद स्प्राउट्स (24g प्रोटीन) 2 उबले अंडे मोong स्प्राउट्स और ककड़ी के साथ। लो GI, रात के लिए परफेक्ट। मूंग दाल चटनी (20g प्रोटीन) भुनी मूंग दाल पीसकर दही में मिलाएं। हल्का और प्रोटीन पैक। सोया चंक्स सलाद (26g प्रोटीन) भिगोए सोया चंक्स को टमाटर-खीरे के साथ। हाई प्रोटीन, जीरो शुगर। डायबिटीज में फायदे ये स्नैक्स इंसुलिन सेंसिटिविटी बढ़ाते हैं और सुबह के स्पाइक्स 30% तक घटाते हैं। भारतीय स्टेपल्स जैसे पनीर, दाल इस्तेमाल करें। CGM से ट्रैक करें व्यक्तिगत प्रभाव। उपयोग टिप्स सोने से 1-2 घंटे पहले लें। 20g+ प्रोटीन लक्ष्य रखें। शुगर-फ्री रखें, वसा/फाइबर जोड़ें।

Protein Powder and CGM: What Your Glucose Curve Reveals About Different Protein Types
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) reveal how protein powders impact blood sugar in real-time, showing spikes from gluconeogenesis even in low-carb options. Different types like whey isolate vs. casein produce varied curves, helping diabetics personalize intake. Protein's Hidden Glucose Impact Protein converts to glucose via gluconeogenesis, especially fast-digesting powders, causing unexpected rises tracked by CGM. Hydrolyzed proteins absorb rapidly, mimicking carbs with insulin spikes similar to white bread. Whole-food proteins digest slower, yielding flatter curves. Whey vs. Casein Curves Whey protein spikes insulin quickly, reducing post-meal glucose in type 2 diabetes but may elevate levels in some. Casein, slower-digesting, shows gradual rises over hours for steady control. CGM data: Whey peaks at 30-60 mins; casein minimal early spike. Plant-Based Protein Patterns Pea or rice proteins often cause milder spikes due to fiber, but added sugars spike curves sharply. CGM users report 20-40 mg/dL rises vs. 50-100+ for whey isolates in sensitive individuals. Check labels to avoid maltodextrin. CGM Insights from Real Users Diabetes forums note 50-60% of protein grams as carbs for dosing; e.g., 30g protein = 15g carb equivalent. Curves flatten with fats/fiber pairing. Track 2-hour post-shake for patterns. Best Picks for Flat Curves Choose unsweetened whey isolate or casein for lowest impact; test personally via CGM. Indian brands like AS-IT-IS offer clean options without fillers. Avoid flavored with hidden carbs. Tips for Testing Dose insulin for 50% protein as carbs if spikes >30 mg/dL. Pair with greens/nuts to blunt rises. Log curves in apps like Dexcom for trends. https://www.yourdiabetesinsider.com/blog/protein-powder-spikes-blood-sugar https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4620107/ https://theorganicproteincompany.co.uk/blogs/health-wellness/can-a-diabetic-use-protein-powder https://asitisnutrition.com/blogs/health/protein-powders-for-diabetics-safe-or-not https://www.netmeds.com/c/health-library/post/are-protein-powders-safe-for-diabetes-types-benefits-uses-and-precautions

High-Protein Breakfasts That Prevent Mid-Morning Blood Sugar Spikes
High-protein breakfasts stabilize blood sugar by slowing carb digestion and promoting satiety, reducing mid-morning spikes common in diabetes. These Indian-friendly recipes deliver 20-30g protein per serving with low-GI ingredients. Why Protein Prevents Spikes Protein at breakfast sustains energy and blunts glucose rises, as it digests slower than carbs. Studies show 30g+ protein curbs hunger and keeps levels steady until lunch. [ from prior] Pair with fiber and fats for optimal control in prediabetes or diabetes management. 5 Quick Recipes Paneer Bhurji with Veggies (25g Protein) Sauté 100g crumbled paneer, onions, tomatoes, spinach, and green chilies. Add turmeric; serve with 1 egg white omelet. Prep: 10 mins. Low-carb, high-fiber to avoid spikes. Moong Dal Chilla (22g Protein) Blend soaked moong dal into batter with ginger and coriander; cook like pancakes. Top with curd. High fiber slows glucose release. Serves 2; ready in 15 mins. Greek Yogurt Parfait (28g Protein) Layer 200g plain Greek yogurt, almonds, chia seeds, and berries. No added sugar; chia adds fiber for steady levels. Prep: 5 mins, overnight optional. Egg and Sprouts Scramble (30g Protein) Scramble 3 eggs with moong sprouts, capsicum, and mushrooms. Use minimal oil. Protein-fat combo prevents post-meal jumps. Done in 8 mins. Besan Cheela with Paneer Stuffing (24g Protein) Mix gram flour batter; stuff with grated paneer and onions. Pan-fry lightly. Chickpea protein stabilizes Indian breakfasts. Benefits for Indians with Diabetes These use affordable desi staples like dal, paneer, and besan for blood sugar control. Aim for 25-30g protein to enhance insulin sensitivity. [ from prior] Tips for Success Eat protein first in meal sequence. [ from prior] Track with CGM for personal spikes. [ from prior] Avoid hidden sugars in store-bought items. [ from prior] https://www.milkandhoneynutrition.com/diabetes-breakfast-recipes-low-carb-high-protein-and-more/ https://www.eatingwell.com/high-protein-breakfast-recipes-for-insulin-resistance-11914756 https://deepahospital.in/blogs/diabetic-indian-breakfast-recipes/