Welcome to the world of sugar free joy!
Low Carb Sugar-Free Sweets & Cakes
Artinci was born out of Aarti's and Sumit's (Artinci's founders) abiding love for great-tasting dessert, while helping them stay committed to their health goals as well. As a result, Artinci makes delicious desserts with zero sugar, that are science and evidence-backed.
Aarti and Sumit come from a family of three generations of diabetics. They were themselves diagnosed pre-diabetic in 2012, and right there began a lifelong quest of a healthy, active lifestyle, including healthy swaps in food
Sugar free Sweets & Cakes



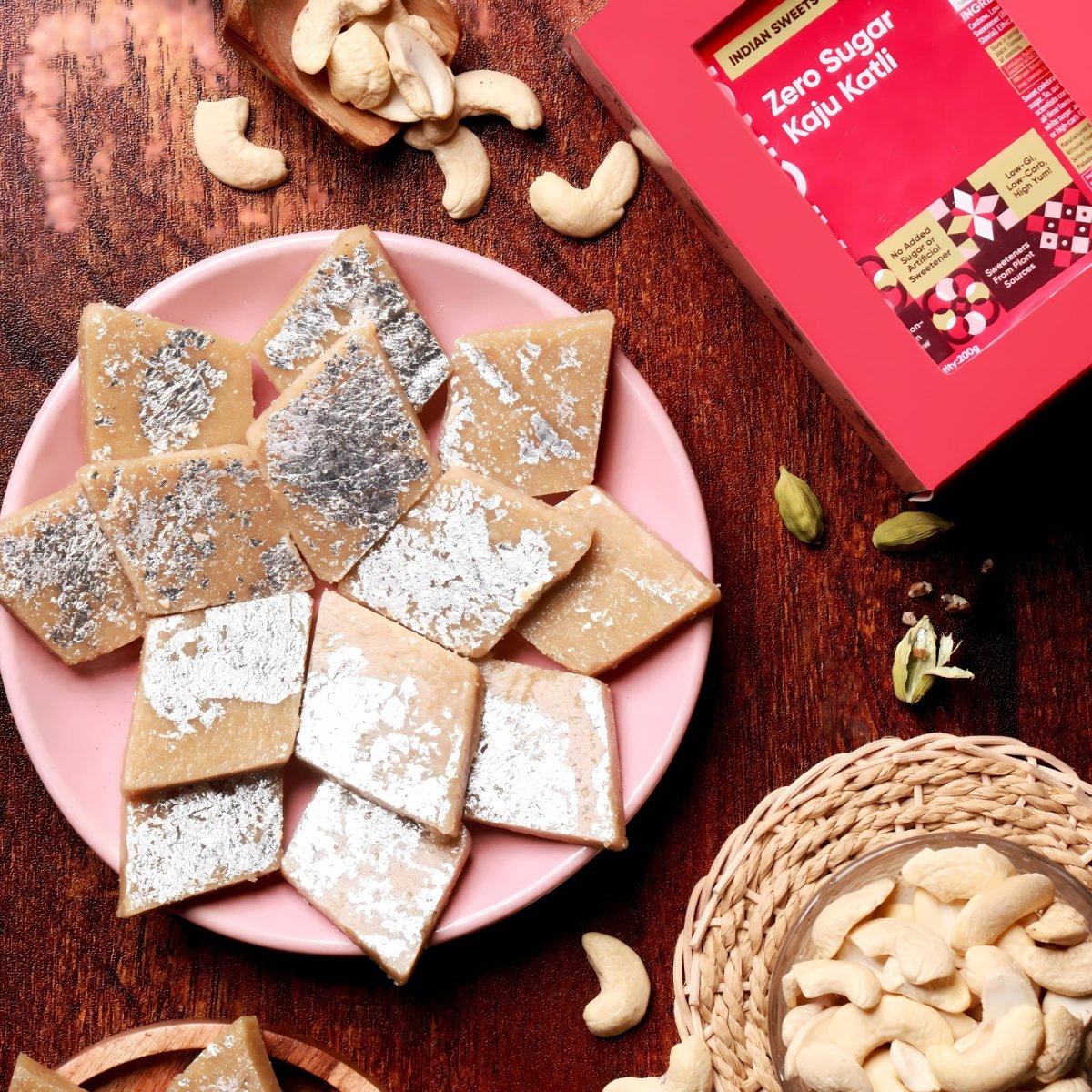
Sugar Free Kaju Katli (Stevia Sweetened) | Keto, Vegan & Diabetic Friendly Sweet | No Maltitol

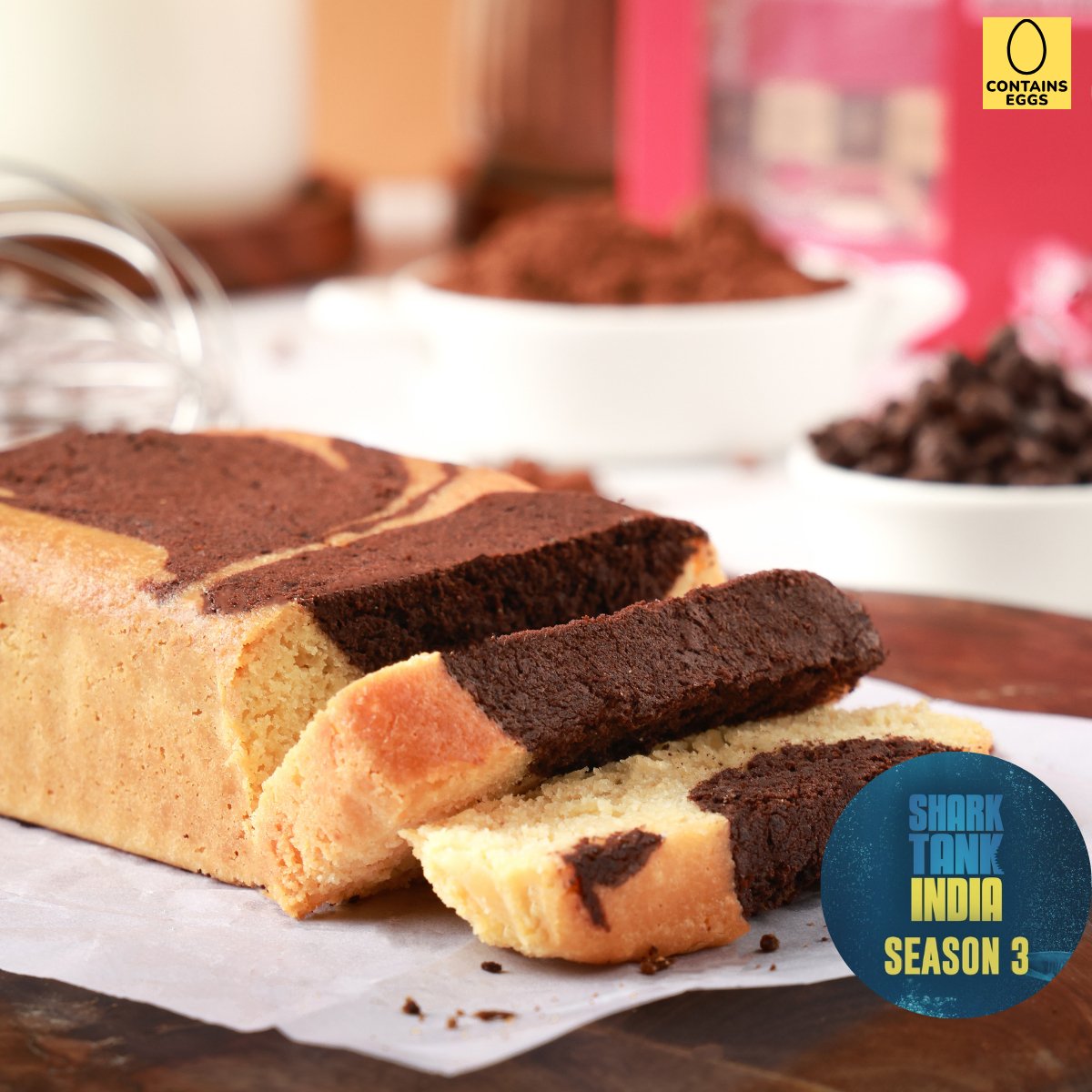
Vanilla & Chocolate Marble Sugar free Cake - Diabetic-Friendly, Keto, Gluten-Free (contains egg)



Aarti Laxman (Founder)
Artinci is founded by Aarti Laxman, a certified Metabolic coach in the Low-Carb Nutrition & Metabolic Health domain from dLife.in, India’s only legally tenable course in this subject—recognized by the NSDC (under the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship, Govt. of India). It’s also internationally accredited by the CPD Standards Office UK, with a global record of 144 CPD hours—the highest for any course of its kind. The accreditation is both nationally valid and globally recognised in over 50+ countries..
Festive Gifting in Artinci
Let customers speak for us
All about Sugar and sugar-free

High sugar intake significantly elevates the risk of cardiovascular disease through multiple metabolic pathways. This blog details the evidence-based dangers, mechanisms, and actionable insights, drawing from recent studies on added sugars and heart health. Metabolic Disruptions Excess added sugars like fructose overload the liver, boosting triglyceride production and fat accumulation in arteries.This raises LDL cholesterol while lowering protective HDL, accelerating plaque buildup and atherosclerosis.Studies show diets with over 17-21% calories from sugar increase CVD mortality by 38% compared to 8%. Hypertension and Stroke Risk High sugar consumption independently elevates blood pressure via insulin resistance and sodium retention.For every 5% increase in free sugar energy intake, stroke risk rises 10% and heart disease by 6%.Sugar-sweetened beverages amplify this, linking to ischemic stroke and abdominal aortic aneurysm. Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Sugar fuels chronic low-grade inflammation, a core driver of endothelial dysfunction and heart failure.Elevated markers like CRP correlate with high intake, worsening outcomes even in normal-weight individuals.This pathway triples CVD death risk at 25%+ calorie intake from added sugars. Obesity-Independent Effects Even without weight gain, high sugar disrupts lipid profiles and promotes de novo lipogenesis in the liver.Regular soda drinkers face higher heart failure risk, independent of traditional factors like cholesterol.Nordic studies confirm sugar's role in dyslipidemia and blood pressure beyond calorie excess. Hidden Dangers in Daily Diets Processed foods and drinks contribute 90% of excess sugar, often exceeding WHO's 10% daily limit unnoticed.Indian staples like sweetened chai or mithai can push intake to risky levels, mirroring global trends.Limiting to under 10% energy from sugar halves CVD markers like triglycerides. 1.https://www.ceu.ox.ac.uk/news/free-sugars-are-associated-with-a-higher-risk-of-cardiovascular-disease 2. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10910551/ 3. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33612591/ 4. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/1819573

Natural Ways to Reduce Sugar Intake for Heart Health
Reducing sugar intake naturally supports heart health by lowering triglycerides, blood pressure, and inflammation risks. This blog explores practical, everyday strategies tailored for Indian lifestyles, focusing on whole foods and habits. Why Cut Sugar for Your Heart Excess added sugars raise bad cholesterol (LDL) and promote artery plaque buildup, increasing heart disease risk.The American Heart Association recommends under 25-36g daily, yet many exceed this via hidden sources like sodas and snacks.Switching to natural methods stabilizes energy and protects cardiovascular function long-term. Swap Sugary Drinks Replace colas and sweetened chai with infused water using lemon, mint, or cucumber for flavor without calories.Opt for black tea or green tea; add ginger or cardamom instead of sugar to curb sweet cravings naturally.This cuts 10-20 tsp of sugar daily from beverages alone, easing heart strain. Choose Whole Foods Prioritize fiber-rich options like millets (ragi, bajra), lentils, and veggies to slow sugar absorption and fullness.Snack on fresh fruits, nuts, or yogurt with cinnamon rather than biscuits or mithai.Whole grains like brown rice over white stabilize blood sugar, reducing heart inflammation. Use Natural Sweeteners Sparingly Incorporate stevia leaves or monk fruit extract for tea; they don't spike blood sugar like refined sugar.Flavor oats or curd with fruits' natural sweetness—berries, apples, or guava—for antioxidants that aid heart health.Limit jaggery to small amounts in traditional sweets, as even natural sugars add up. Mindful Eating Habits Eat smaller, frequent meals with protein (dal, paneer) and fiber to prevent sugar binges.Read labels: Avoid products with >6g sugar per serving; choose unsweetened curd or nut butters.Combine with 30-min walks post-meals to enhance insulin sensitivity and heart fitness. Quick Recipes to Try Cinnamon Apple Oats: Cook oats with chopped apples, cinnamon, and a dash of nuts—no added sugar needed.Minty Buttermilk: Blend curd, mint, cumin, and roasted jeera for a cooling, savory drink.These keep meals tasty while slashing sugar by 50% effortlessly. Long-Term Benefits Consistent changes lower HbA1c and triglycerides within weeks, slashing heart attack risk.Track progress with a food diary; taste buds adapt in 2-4 weeks, making sweets less appealing.Pair with stress relief like yoga for holistic heart protection. https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/14-ways-to-lower-blood-sugar https://www.heartandstroke.ca/healthy-living/healthy-eating/reduce-sugar https://www.pennmedicine.org/news/5-ways-to-reduce-sugar-in-your-diet

Sugar कैसे बढ़ाता है सूजन: साइटोकाइन्स, डायबिटीज प्रभाव और उपाय
अधिक शुगर (खासकर फ्रक्टोज) हाइपरग्लाइसीमिया पैदा करता है, जो साइटोकाइन्स IL-6, TNF-α और CRP को बढ़ाता है। यह NF-κB पाथवे सक्रिय कर क्रॉनिक इंफ्लेमेशन शुरू करता है, इंसुलिन रेसिस्टेंस बढ़ाकर टाइप 2 डायबिटीज को बढ़ावा देता है। अध्ययनों से साबित है कि हाई ग्लूकोज PBMCs में प्रो-इंफ्लेमेटरी साइटोकाइन्स बढ़ाता है। तले हुए खाद्य पदार्थों का जोखिम तले खाद्य में शुगर + ट्रांस फैट AGEs बनाते हैं, जो गट बैक्टीरिया बिगाड़कर सूजन फैलाते हैं। समोसे या पकौड़े ब्लड शुगर स्पाइक के साथ साइटोकाइन्स रिलीज करते हैं, डायबिटीज में हृदय/किडनी क्षति बढ़ाते हैं। बेक्ड विकल्प चुनें। एंटी-इंफ्लेमेटरी काउंटर उपाय उपाय कैसे काम करता है भारतीय उपयोग हल्दी (कर्क्यूमिन) साइटोकाइन्स TNF-α रोकता है हल्दी दूध, सब्जी अदरक IL-6 कम करता है चाय, करी हरी सब्जियां (पालक) एंटीऑक्सीडेंट्स सलाद, स्मूदी ओमेगा-3 (अलसी) सूजन मार्कर्स घटाते चटनी, रोटी प्रोबायोटिक्स (दही) गट हेल्थ सुधार रायता ये शुगर के प्रभाव को 30% तक कम कर सकते हैं। रोज 2 सप्ताह में CRP टेस्ट से ट्रैक करें। डायबिटीज रोगियों के लिए टिप्स शुगर काटें (स्टेविया अपनाएं), तला हुआ छोड़ें। योग/वॉकिंग जोड़ें। डॉक्टर से CRP जांच करवाएं। संतुलित डाइट से सूजन नियंत्रित रखें। https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6119493/ https://www.lalpathlabs.com/blog/does-sugar-cause-inflammation-in-the-body/ https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/sugar-and-inflammation https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/inflammation-and-diabetes

डायबिटीज में वेज बनाम नॉन-वेज प्रोटीन स्रोत: पूरी तुलना
डायबिटीज में प्रोटीन की भूमिका प्रोटीन ब्लड शुगर स्पाइक रोकता है, इंसुलिन संवेदनशीलता बढ़ाता है और वजन नियंत्रित रखता है। टाइप 2 मधुमेह में दैनिक 0.8-1 ग्राम/किलो वजन लें, लेकिन स्रोत का चुनाव महत्वपूर्ण। वेज स्रोत प्लांट-बेस्ड फाइबर देते हैं, नॉन-वेज अमीनो एसिड पूर्ण होते हैं। किडनी प्रभावित होने पर प्रोटीन सीमित करें। वेज vs नॉन-वेज: विस्तृत तुलना पैरामीटर वेज प्रोटीन (दाल, पनीर, सोया) नॉन-वेज प्रोटीन (चिकन, मछली, अंडा) डायबिटीज प्रभाव प्रोटीन मात्रा (प्रति 100g) 20-25g (चना: 19g, पनीर: 18g) 25-30g (चिकन: 27g, मछली: 25g) दोनों समान, लेकिन वेज धीमा अवशोषण ब्लड शुगर प्रभाव कम GI, फाइबर से स्थिर शुगर न्यूट्रल, लेकिन तला हुआ स्पाइक बढ़ाए वेज बेहतर लंबे नियंत्रण के लिए फायदे हृदय-अनुकूल, सस्ता, गट हेल्थ मसल बिल्डिंग तेज, विटामिन B12 वेज सूजन कम, नॉन-वेज ऊर्जा नुकसान अपूर्ण अमीनो, अधिक मात्रा गैस कोलेस्ट्रॉल, यूरिक एसिड जोखिम नॉन-वेज किडनी पर बोझ यदि अधिक लागत (भारतीय बाजार) ₹50-100/kg ₹200-400/kg वेज बजट-अनुकूल वेज हृदय रोगियों के लिए सुरक्षित, नॉन-वेज व्यायाम करने वालों के लिए। भारतीय आहार में उपयोग टिप्स वेज रेसिपीज: मूंग दाल खिचड़ी (25g प्रोटीन), पनीर टिक्का, सोया चंक्स करी। नॉन-वेज रेसिपीज: ग्रिल्ड चिकन सलाद (30g), भाप मछली, उबले अंडे।हर मील में 20-25g प्रोटीन मिलाएं। शाकाहारी 70% वेज चुनें। सावधानियां किडनी समस्या (नेफ्रोपैथी) में नॉन-वेज कम करें। लाल मांस (मटन) से बचें। डॉक्टर से GFR जांच करवाएं। संतुलित प्लेट: ½ सब्जी, ¼ प्रोटीन, ¼ साबुत अनाज। 1. https://www.tv9hindi.com/webstories/health/veg-or-non-veg-which-protein-is-good-for-health 2. https://ndtv.in/food-lifestyle/diabetes-diet-should-diabetics-not-eat-protein-rich-foods-does-high-protein-raise-blood-sugar-levels-does-protein-affect-blood-sugar-levels-2969472 3. https://www.jansatta.com/health-news-hindi/should-not-eat-non-veg-in-diabetes-know-how-your-complete-diabetic-diet/2586889/